Overview
The image below provides a simple overview of the different components in the Raito ecosystem.
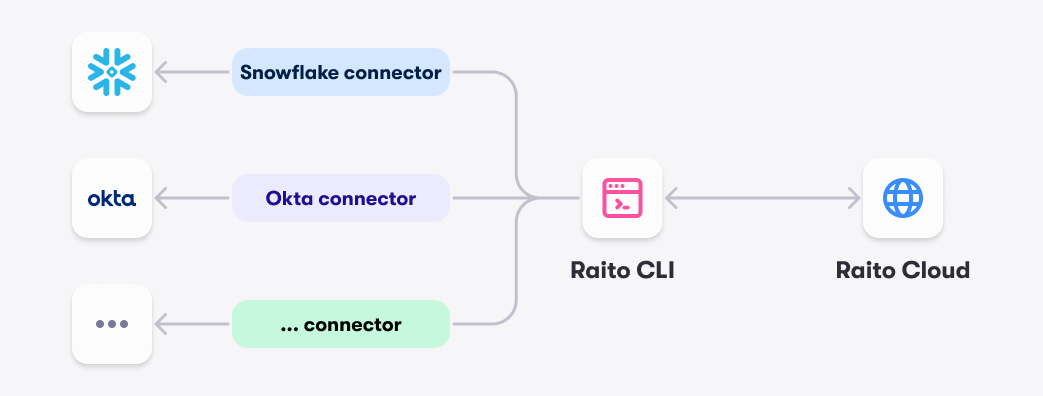
Raito Cloud
The Raito Cloud component, shown at the bottom in the image above, is the SaaS web application that most Raito users will interact with. It provides
- a clear overview of the structure of your data sources
- an overview of who has access to what
- smart insights into the state of your data sources by looking at the access controls and how they compare to the actual usage
- a simple way to update the access to your data sources
- an easy way to request access to data and a guided and automated flow to resolve the requests
- and much more…
There are basically 3 ways to extract data from and manipulate data in Raito Cloud:
- The User Interface, which if explained further in the Raito Cloud section of the documentation.
- The API can be used to integrate 3rd party tools to do things like requesting access, manipulating access controls, extracting information, etc. This is covered in more detail in the API section of the documentation.
- The Raito CLI, which is further explained below.
Raito CLI
The Raito CLI component, shown in the middle of the image above, is the link between your data sources and Raito Cloud. It is an open-source command-line interface application that can run in your data center or even on your own laptop/desktop.
Alternatively, there is an option to run the CLI from within Raito Cloud. This is a good option to get started with Raito quickly, but not recommended for production environments.
While synchronizing with Raito Cloud, the CLI extracts information from the data source. This includes the data objects (e.g. the databases, schemas, tables, … present), the identities (users and groups), the existing access controls (e.g. Snowflake roles) and the data usage information. In the other direction, the access controls defined in Raito Cloud are pushed to the data source (e.g. by creating and updating Snowflake roles).
The Raito CLI is fully open-source to provide full transparency into what information is extracted from the data sources and sent to Raito Cloud.
Connector
The connection to a data source itself happens in a connector, which is a plugin of the CLI. Each type of data source will have its own connector. Raito will provide some connectors as open-source, but it’s perfectly possible to implement your own connector for data sources that are not supported by Raito yet.
On the top of the image above, we see the data sources (also called targets) that the connectors will connect with.
More details can be found in the Raito CLI section.